TGPT-1D
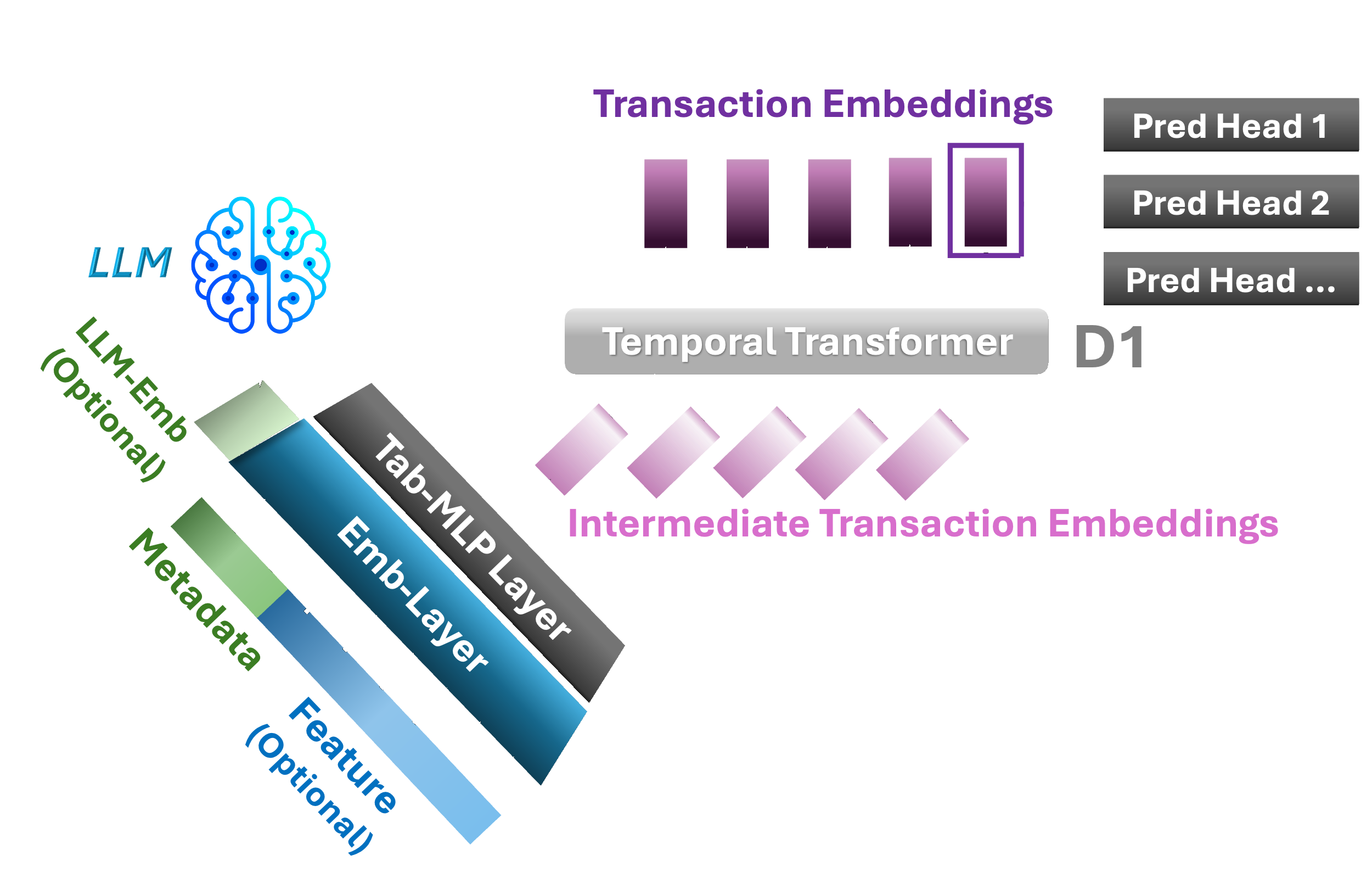
A GPT-style decoder-only Temporal Transformer with local attention (window w) and a tabular MLP. Processes each transaction embedding as a token for auto-regressive generation.
TGPT-2D
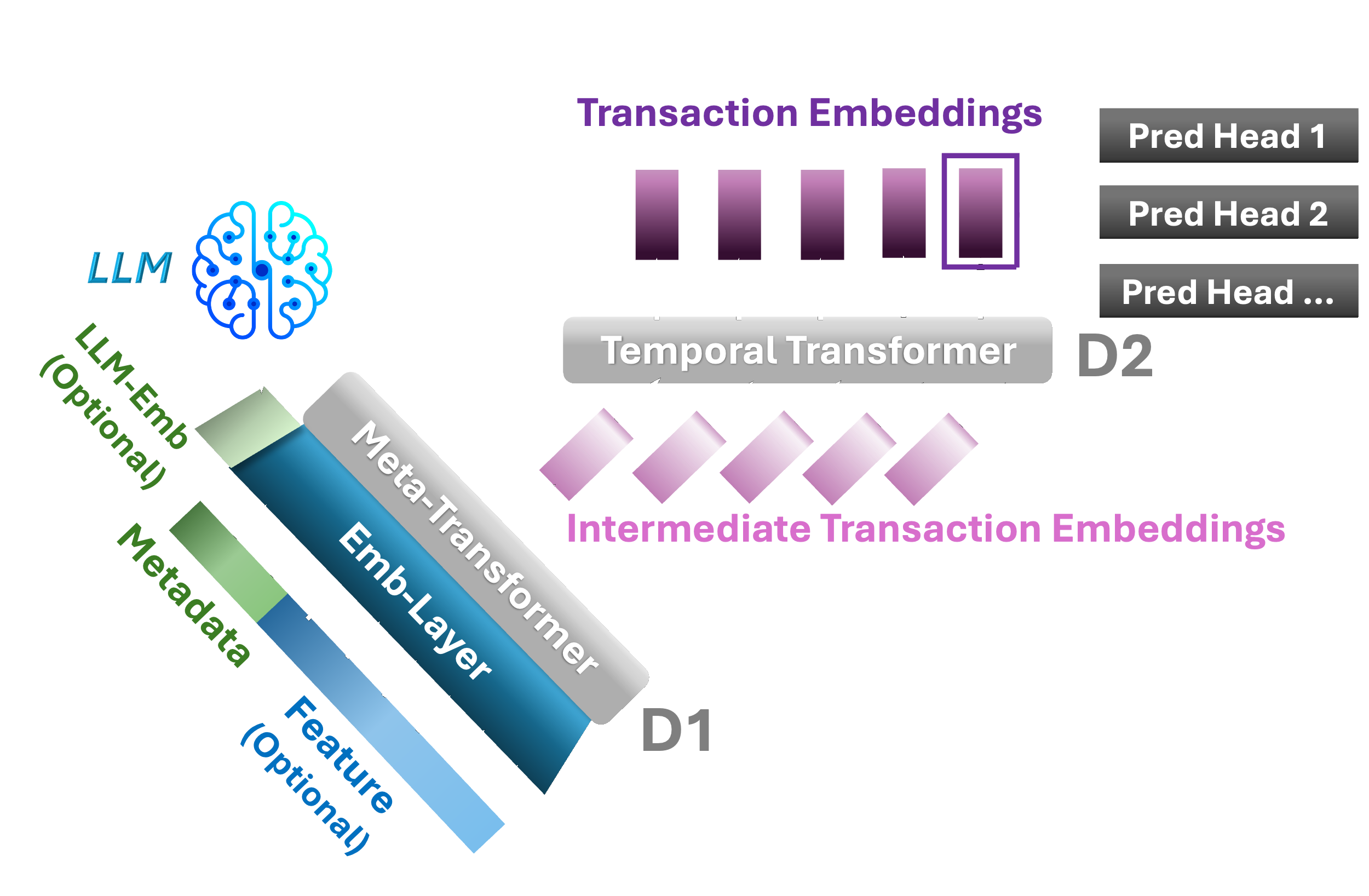
Adds a bidirectional encoder-only Metadata Transformer that replaces the MLP, modeling cross-field interactions across merchant category, amount, and location with compositional embeddings for high-cardinality entities.
TGPT-3D
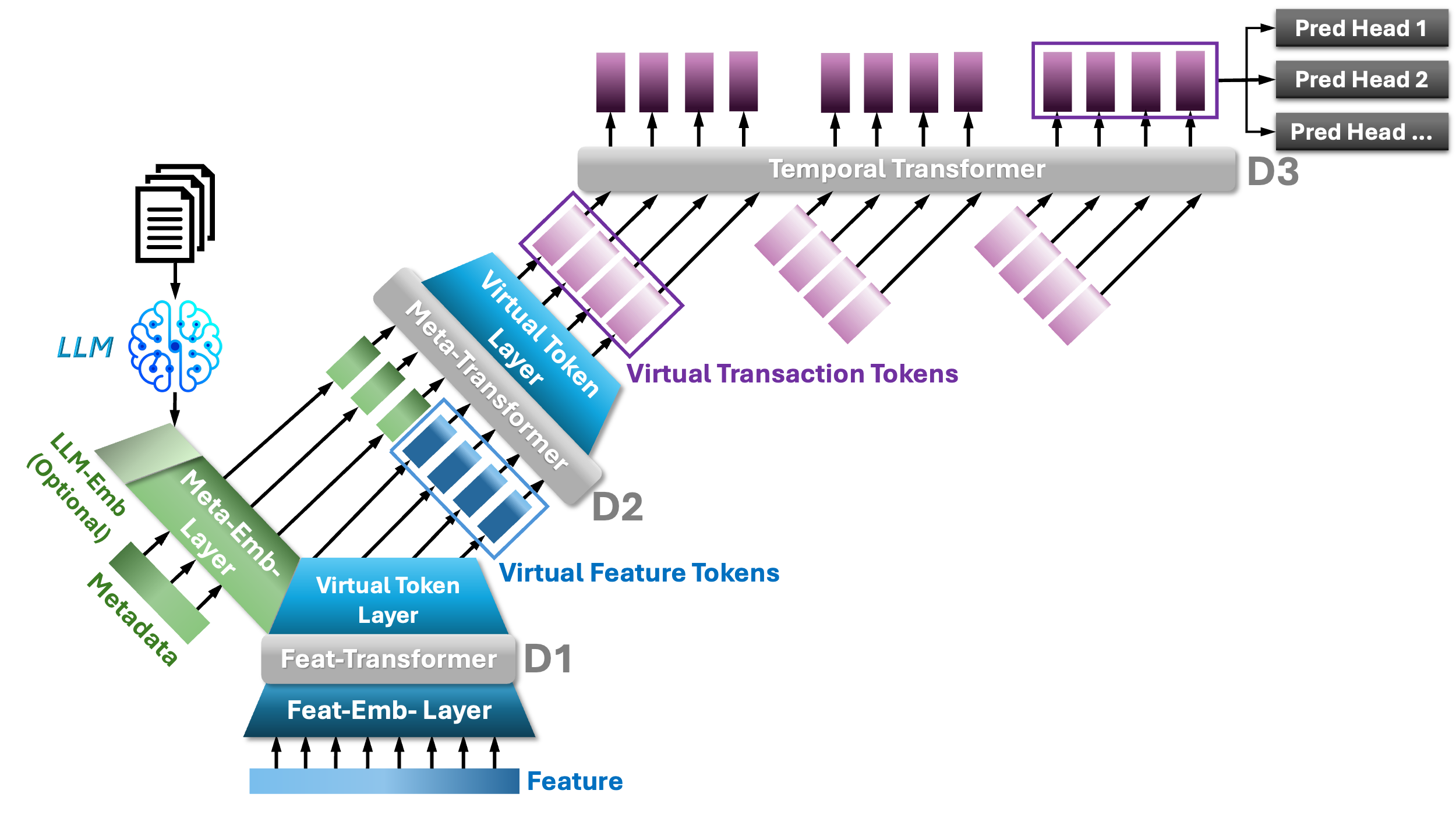
A separate Feature Transformer encodes hundreds of downstream features with optimally-sized small embeddings. Two variants — MTF (sequential) and FMT (with Virtual Token Layer) — enable effective cross-modality fusion.
Virtual Token Layer (VTL)
The key innovation enabling effective modality fusion across the 3D architecture. Inspired by ResNet, VTL uses dual channels: a linear path to preserve gradient flow and a nonlinear path for expressiveness.
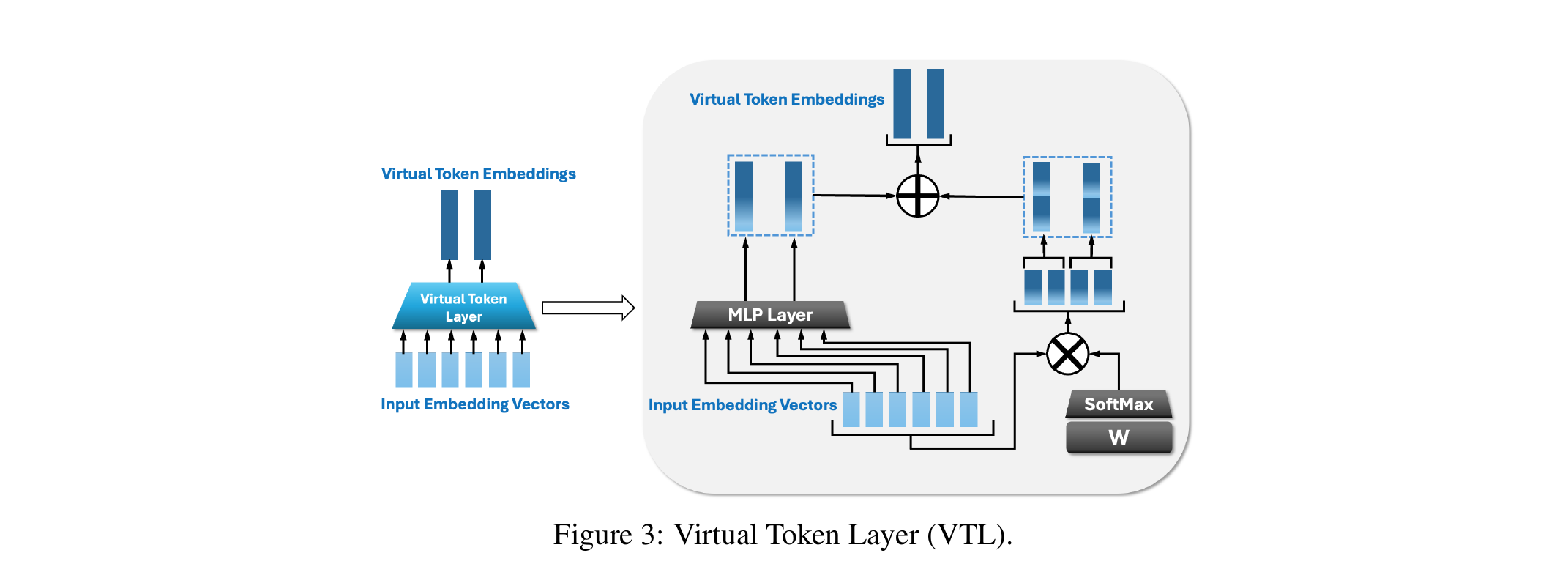
Linear Channel
Weighted combination preserves gradient flow and ensures stable training through direct information pathways.
Nonlinear Channel
MLP with activation rescales to any target dimension, enhancing expressiveness while decoupling bandwidth from embedding size.
Step 1: Feature → Transaction
Virtual Feature Tokens compress feature embeddings to match metadata dimension (dM)
Step 2: Transaction → Temporal
Virtual Transaction Tokens convert each transaction into vt tokens for the Temporal Transformer